Who we are
ECDC's organisational structure
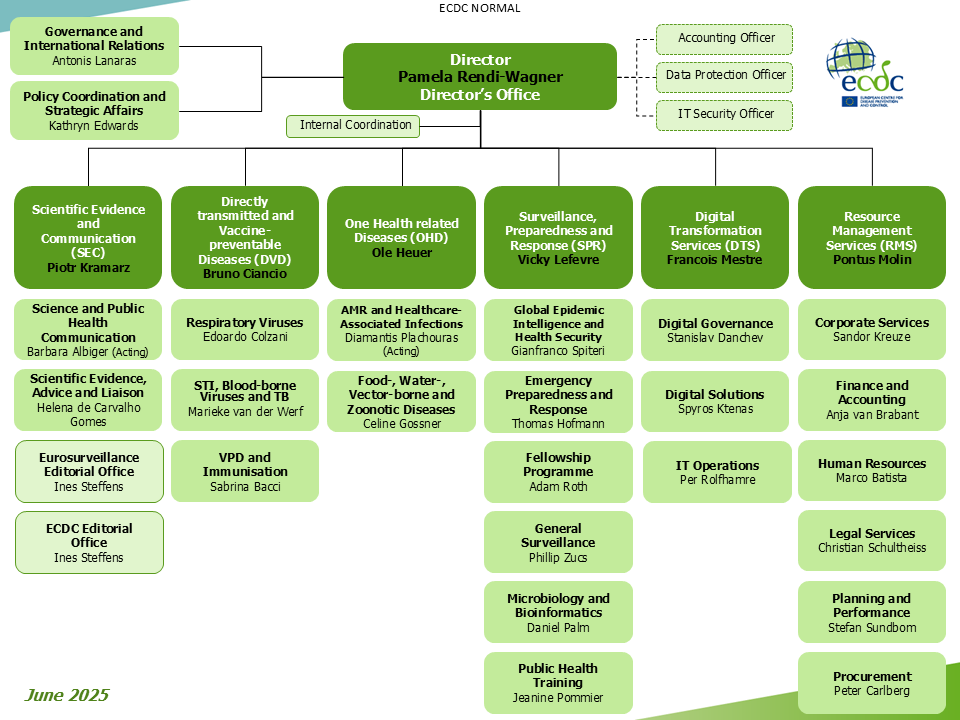
Director's office
The entities in the Director’s Office are functions which are linked to the implementation of the Centre’s strategy: they oversee and coordinate responses to political developments, external relations, important and urgent scientific and public health matters, as well as the high-level management of the internal workings of the Agency. The Director’s Office provides the central coordination of the Centre’s external strategic relationships inside the EU to Member States (MS), Advisory Forum (AF), Management Board (MB), Coordinating Competent Bodies (CCB) and to EU institutions (European Commission, European Parliament, Council, other agencies), as well as outside the EU (EU enlargement (ENL), European Neighbourhood Policy Partner (ENP) countries), and partners with whom ECDC holds a Memorandum of Understanding (WHO, other CDCs). The actual implementation and the monitoring of the work is done in the Units.
The Data Protection Officer, Accountant and IT Security Officer report directly to the Director in those specific functions. The work in the Director’s Office is carried out in two Sections:
-
Governance and International Relations: The Section serves as a central entry point for all ECDC’s strategic relations with the EU Commission services, European Council, ENL and ENP countries, WHO and other CDCs. It also coordinates ECDC’s country support by being the central entry point and monitors the implementation of the support activities. The operational activities are carried out in the respective Units/Sections that work in the area of the requested support. The Section also coordinates all activities with the corporate bodies (MB, AF and CCB), as well as ensures the coordination of the Director’s Consultation Groups (DCG).
-
Policy Coordination and Strategic Affairs: The Section serves as a central entry point for all ECDC’s strategic relations with key EU institutions, including the European Commission, European Parliament, EU Agencies, the EU Agencies Network (EUAN), and other actors relevant to the strategic work of ECDC and the Director. The Section supports policy and strategic engagement of the Director and is responsible for overall external policy coordination. The Section is also responsible for developing ECDC’s strategic and policy positioning and activities, with a particular focus on key EU policy and legislative files and on bridging between science and policymaking. It also develops science policy studies and handles policy communications activities for the ECDC Director and conducts stakeholder engagement and intelligence gathering activities aimed to profile and promote the work of the Centre.
Scientific Evidence and Communication (SEC)
Led by the Chief Scientist, the Unit defines and steers ECDC’s scientific strategy, ensuring coherence, quality, integrity and independence across ECDC’s work. In liaison with other Units and European and international partners, SEC anticipates future needs and supports the Chief Scientist in providing cross-unit direction to align ECDC’s scientific and public health activities with evolving priorities and emerging threats, promotes consistency and transparency in scientific processes, and safeguards the integrity, relevance, independence and impact of the Centre’s public health outputs. The Unit oversees the Centre’s evidence pathway, from evidence generation, analysis, critical appraisal and synthesis to translation into timely, clear and actionable public health risk assessments, recommendations and communication outputs to support timely and transparent evidence-informed decision-making and achieve the planned public health impact.
While operational activities lie largely with the disease and public health functions units, SEC ensures the robustness and coherence of the Centre’s processes and outputs, with a strong focus on transparency, quality assurance, strategic foresight and clear communication to change behaviours and inform policy.
The Chief Scientist and SEC play a key role in scientific engagement within and beyond ECDC, acting as knowledge broker and evidence translator, cultivating strategic collaborations with learned societies, professional associations, and research funders to promote applied public health research and strengthen the science-policy-practice interface.
In liaison with other Units and international partners, the Chief Scientist, supported by SEC, provides leadership and strategic advice to the Director and EU research funders on research and innovation, scientific priorities and investments within Centre’s mandate to strengthen ECDC’s scientific workforce and future capabilities. The Unit also leads flagship initiatives such as the annual scientific conference ESCAIDE and hosts the editorially independent scientific journal Eurosurveillance. Finally, the Unit coordinates ECDC knowledge management. The Unit works in two sections and an ECDC editorial office.
Science and Public Health Communication: The Section contributes to the Centre’s mission of communicating ECDC science-based recommendations to the target audiences, promoting European public health and raising ECDC’s visibility through targeted science and corporate communication and adapted channels. It includes the following functions:
-
External Communication ensures that ECDC’s work reaches the wider public, media, and stakeholders.
-
Science Communication, in support to ECDC amended mandate, targeting a non-expert audience, to translate complex public health information and data into accessible, accurate, and engaging messages to help better understand public health threats.
-
Crisis and Risk Communication in support to the European Commission and the Member States in the context of the amended mandate and serious cross-border threats to health regulation, provides timely, accurate information, FAQs, real-time updates, and guidance on public health interventions. This function is particularly crucial during public health emergencies and promotes protective behaviours and trust.
-
Corporate Communication shapes how ECDC is perceived globally. It supports the organisation’s goals by building trust, aligning messaging with core values, and enhancing the Centre’s reputation.
-
Health Communication seeks through vaccination campaigns, awareness days, health literacy initiatives, and behaviour change messaging to increase public awareness and to influence behaviour that could improve health outcomes.
-
Internal Communication plays a vital role in keeping staff informed and engaged through regular updates, leadership messages, internal newsletters, and staff campaigns. It aims to foster a unified organisational culture and supports collaboration across teams.
Together, these communication functions ensure that ECDC’s work is visible, credible, and impactful - both within the organisation and across the public health landscape. The Section works in close collaboration with ECDC editorial office, technical experts and disease programme leads as well as the Director’s office.
Scientific Evidence, Advice and Liaison: The Section plays a central role in strengthening the Centre’s evidence ecosystem and scientific principles. It supports the Chief Scientist’s scientific strategy and priority-setting, and drives strategic initiatives that ensure the scientific integrity, relevance and cross-unit coherence of ECDC’s public health outputs, and is responsible for related policies, procedures and tools, including the Centre’s scientific output management and repository system (SARMS). The Section leads on the development and application of evidence and quality assurance frameworks, coordinates methodological development, and promotes integrated, interdisciplinary approaches for evidence generation, synthesis and translation, supporting the production of highquality, evidence-based public health advice and contributing to the ECDC’s role as a credible and trusted source of public health knowledge. With biostatistics and mathematical modelling capacities now distributed across disease specific units, the Section retains a coordination function for these areas, while expanding its role in social, behavioural and implementation sciences and hosting ECDC’s library and scientific information services. The Section supports internal and external scientific engagement and acts as knowledge broker between ECDC and the wider public health community, developing and maintaining active partnerships with learned societies, professional associations, research networks and funders, and promotes and strengthens the public health science-policy practice interface through strategic foresight and anticipation. It also organises key initiatives such as ECDC’s annual scientific conference ESCAIDE, fostering dialogue and collaboration across countries and between public health researchers, practitioners and decision-makers.
The ECDC Editorial Office provides editorial services for ECDC.
In addition, the Eurosurveillance Editorial Office is hosted in the Scientific Evidence and Communication Unit. The Eurosurveillance Editorial Office is responsible for the independent scientific journal on surveillance, prevention and control of infectious diseases published by ECDC. As diamond open access journal, it provides a platform for exchange of scientific disease information among experts in Europe and worldwide, free of charge for readers and authors.
Directly Transmitted and Vaccine-preventable Diseases (DVD)
As one of two disease units, this Unit will provide relevant, timely and useful science-based risk assessments and recommendations to inform public health policy making and response measures to prevent and control infectious diseases in the EU. It will promptly and effectively detect, respond to and control outbreaks and other infectious disease threats in the EU and contribute to the establishment of solid and sustainable capacities and infrastructures for surveillance, prevention, preparedness, applied research, and response in the EU countries and institutions. The Unit will define and implement surveillance priorities, strategies and standards, conduct surveillance, data analysis and interpretation, and based on this identify actionable prevention and control strategies for diseases under its remit.
The Unit is organised in three Sections.
Respiratory Viruses: The Section is responsible for all prevention and control activities of the Centre on viral respiratory infections, including (but not limited to) influenza, SARS-CoV2 and RSV. Such activities encompass disease surveillance, monitoring of public health prevention and control programmes and evaluation of their impact, and provision of scientific advice to Member States and EU institutions on recommended measures to prevent and control ongoing, emerging and expected respiratory infections threats. Furthermore, the Section aims at informing EU/EEA and national public health policy making for effective prioritisation of resources and for achieving the intended public health targets. Since most of the diseases under the remit of the RV Section are international threats, the Section works in close collaboration with external partners such as WHO, regional and national CDCs, other EU agencies and the disease networks in the Member States. The Section is highly involved in the support of laboratory and diagnostic activities concerning respiratory viruses and in activities related to pandemic preparedness and response against zoonotic respiratory viruses with a One Health perspective.
STI, Blood-borne Viruses and TB: The Section is responsible for all prevention and control activities of the Centre on infections that are transmitted directly through sexual contact, blood, or the use of substances of human origin (SoHO), and on tuberculosis (TB). Such activities encompass disease surveillance, monitoring of public health prevention and control programmes and evaluation of their impact, and provision of scientific advice to Member States and EU institutions on recommended measures to prevent and control ongoing, emerging and expected threats posed by STI, Blood-borne Viruses, TB and SoHO. Furthermore, the Section aims at informing EU/EEA and national public health policy making for effective prioritisation of resources and for achieving the intended public health targets. These include monitoring the progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 3.3) and supporting countries that are lagging behind by scientific advice and tailored country support, and achieving the WHO elimination targets for hepatitis B and C, and for tuberculosis. The Section has a strong focus on fostering the implementation of effective disease prevention programmes and services targeting vulnerable populations in the EU that are at increased risk of infection and severe outcome from SBT diseases and that are often hard to reach by untargeted measures. To achieve its goals the Section collaborates with external partners such as WHO, other EU or UN agencies and NGOs, while being in close partnership with disease networks and the European Commission. The Section also coordinates the ECDC work on substance of human origin (SoHO).
VPD and Immunisation: The Section is responsible for all activities of the Centre on diseases that are preventable by vaccination and predominantly transmitted by direct person to person contact. It also provides expert advice for diseases that are vaccine preventable or against which new vaccines are expected to become available, but that are under the remit of other disease Sections in the Centre. Main activities of the Section include disease surveillance, monitoring of vaccination programmes and evaluation of their impact, and provision of vaccine and immunisation recommendations to Member States and EU institutions, particularly when new vaccines are introduced in the market or in response to signals of reduced vaccination programme effectiveness. Furthermore, the Section aims at informing EU/EEA and national public health policy making for effective prioritisation of resources and for achieving the intended vaccine coverage targets, including through fostering vaccine acceptance by the population. It also supports Member States in their efforts to reach related eradication/elimination targets by scientific advice and tailored country support. Disease network meetings for the specific diseases are held regularly for information and good practice exchange. Since most of the diseases under the remit of the VPI section are international threats, the Section works in close collaboration with external partners, particularly with EMA, the NITAGs, WHO, and the disease networks in the Member States. Furthermore, the VPI Section implements the ECDC-related parts of the Council Recommendations (2018), on strengthened cooperation against vaccine-preventable diseases including among others, the creation and establishment of EVIS (European Vaccination Information Sharing), and the European Vaccination Information Portal.
One Health related Diseases (OHD)
As one of two disease units, this Unit will provide relevant, timely and useful science-based risk assessments and recommendations to inform public health policy making and response measures to prevent and control infectious diseases in the EU. It will promptly and effectively detect, respond to and control outbreaks and other infectious disease threats in the EU and contribute to the establishment of solid and sustainable capacities and infrastructures for surveillance, prevention, preparedness, applied research, and response in the EU countries and institutions. The unit will define and implement surveillance priorities, strategies and standards, conduct surveillance, data analysis and interpretation, and based on this identify actionable prevention and control strategies for diseases under its remit.
The Unit is organised in two Sections, which are supported by the horizontal function on One Health, providing coordination and support in the respective areas across the Centre through a One Health working group, and facilitating cross-agency One Health coordination between ECDC and other EU agencies.
AMR and Healthcare-associated Infections: The Section validates, analyses, and interprets surveillance data, assesses, and communicates the results in order to provide evidence for policymaking and action at EU and country level, and improves surveillance systems for AMR, antimicrobial consumption and HAIs in collaboration with external partners (WHO, other EU or UN agencies) in a One Health perspective where appropriate. It implements the ECDC related parts of EU and global action plans. It supports Member States in their efforts to prevent and control AMR and HAIs by scientific advice and tailored country support. Disease network meetings are held regularly for information and good practice exchange.
Food-, Water-, Vector-borne and Zoonotic Diseases: The Section validates, analyses and interprets surveillance and monitoring data, and performs scientific assessments and reviews of the evidence in relation to emerging, food-, water- and vector-borne diseases as well as zoonotic diseases, to inform policy makers, public health authorities and other relevant target audiences. Many of these diseases are affected by climate change, and the Section is engaged in cross sectoral collaboration to address its impact on infectious diseases in a One Health perspective. Activities are performed in collaboration with external partners, particularly EFSA, EEA, EC and WHO, the EURL-PH and three disease networks composed of Member States representatives. The Section supports Member States in the coordination of (potential) cross-border health threats, and strengthens their capacity to prevent, detect and respond to outbreaks.
Surveillance, Preparedness and Response (SPR)
The Surveillance, Preparedness and Response Unit is responsible for the standardisation, integration, implementation and coordination of surveillance, epidemic intelligence, microbiology, bioinformatics, emergency preparedness, outbreak response and training activities across diseases. It leads horizontal activities, develops cross-cutting public health tools, provides direct support to countries and fosters innovation to strengthen public health capacities and reduce the burden of communicable diseases in Europe. The work to achieve these aims is carried out in six sections:
Emergency Preparedness and Response: The Section coordinates emergency preparedness and outbreak response activities across the Centre. It is responsible for the Emergency Operations Centre, the Public Health Emergency Plan, and the organisation of the Public Health Emergency Preparedness Assessments (PHEPA), simulation exercises and After-Action reviews. It coordinates the production of Rapid Risk Assessments and supports the European Union Health Task force, providing remote and on-site support to countries in preparedness and outbreak response in collaboration with EU and international partners. The Section is also responsible for the operation, maintenance and further development of the EWRS and serves as focal point for intentional release of biological agents in the frame of CBRN and health security.
Global Epidemic Intelligence and Health Security: The Section performs global threat detection, monitoring and assessment through epidemic intelligence. It organises the daily ECDC round table meetings and produces daily and weekly Communicable Disease Theat Reports. It is responsible for co-ordinating event-based surveillance activities, the operation, maintenance and further development of event-based surveillance systems and tools (EpiPulse Events, EpiPulse CDTR and Epi+) and the implementation of novel technologies and Artificial Intelligence in EI and threat detection. It collaborates with global and regional partners (including GHSI and EIOS) and it contributes to global health security through the implementation of European Commission funded projects with Enlargement and European Neighbourhood Policy countries and Africa CDC.
Fellowship Programme: The Section coordinates, implements and further develops the ECDC Fellowship Programme with a field epidemiology path (EPIET) and a public health microbiology path (EUPHEM). It establishes and maintains a network of appraised training sites in the Member States, to provide high quality supervision and field assignments of public health relevance. The Section keeps the Fellowship Curriculum updated, delivers training to support fellows to successfully conduct the field assignments at the training sites and coordinates international assignments. The Section collaborates with the EPIET Alumni Network and maintains a network of training sites and supervisors through facilitating active participation in teaching and supervision. It also collaborates with global training networks and supports Member States in the development and running of national field epidemiology training programmes.
General Surveillance: The Section coordinates, implements and monitors general surveillance activities across the Centre, including the provision of data science, GIS and data management services. This includes setting the template for surveillance standards and their monitoring, coordinating the routine indicator-based surveillance process, developing and maintaining surveillance systems (EpiPulse Cases, Surveillance Data Warehouse), tools and outputs, and providing scientific support to the European Commission. The Section also coordinates e-Health based surveillance and the ECDC involvement in the European Health Data Space.
Microbiology and Bioinformatics: The Section coordinates and standardises microbiology and bioinformatics activities across diseases. It supports the European Commission in the designation of European Union Reference Laboratories (EURL) and coordinates the Network of EURLs for Public Health. It monitors laboratory capacity in Europe, coordinates wastewater monitoring and the implementation of genomic based typing across diseases. It develops and maintains bioinformatics systems, tools and outputs, organises bioinformatics trainings and provides sequencing support to Member States.
Public Health Training: The Section is responsible for organising, coordinating and supporting the development and implementation of ECDC public health training activities. It ensures alignment, consistency, quality and excellence across all training initiatives organised by the centre. The Section develops and maintains the Learning Portal that showcases ECDC training activities in areas such as preparedness, surveillance, microbiology, One Health, epidemiology, outbreak response, antimicrobial resistance and risk communication. The trainings aim to provide public health professionals across the EU/EEA with the necessary knowledge, skills, and competencies to effectively address current and emerging health threats.
Digital Transformation Services (DTS)
The Unit delivers digital solutions, maintains IT products and provides IT services, which are instrumental to the operation and administration of the Centre. It also provides digital workplace. addressing the needs for mobility, communication and collaboration of staff. The Unit networks with other EU bodies and partners across Europe for topics relevant to digital transformation.
The Unit applies (i) its Target Operating Model, which defines its sourcing model, (ii) the ECDC IT, Governance, which steers the portfolio of IT products and services, which is fit for purpose and addresses business needs. The Unit also applies (iii) its Information Security Management System, (iv) provides advice and studies, (v) front-end services, (vi) application hosting and (vii) enterprise infrastructure services.
The Unit’s work is carried out in three Sections:
Digital Governance: The Section is responsible for the Unit’s strategic and financial planning, enterprise architecture, IT quality and continual service improvement. It also manages the information security management system. In addition, the Section is responsible for strengthening the Centre’s information governance systems and processes to the benefit of internal and external users.
Digital Solutions: This Section is responsible for delivering digital solutions based on business requirements, managing business requirements, defining solution architecture, conducting studies, projects and maintaining IT products for all Units.
IT Operations: This Section provides end user services, application hosting and enterprise infrastructure
services, it aims to build maintainable, compatible and sustainable services, which are scalable according to
operational need.
Resource Management Services (RMS)
The Resource Management Services Unit aims at top quality management of ECDC’s human and financial resources. The Unit’s work is carried out by six sections.
Corporate Services: Corporate Services aims at developing and maintaining the premises of the Centre to meet the requirements of the organisation, providing logistics services for the operational activities and to staff, maintaining the physical inventory and ensuring security. The Section furthermore organises travel and hotel arrangements and provides budget verification, monitoring and supports processing of reimbursement claims for staff, interviewees and experts invited to ECDC with a high level of service attitude and ensuring an economically prudent use of ECDC’s travel budget. The Section furthermore manages the mailroom and archives.
Finance and Accounting: The Finance and Accounting Section aims at ensuring that the financial resources of the Centre are managed efficiently and reported in a clear and comprehensive manner. The Section provides financial initiation and verification of commitments and payments and executes all payments. It also provides the annual accounts of the Centre, which present a true and fair view of the financial position of the Centre. Finance and Accounting ensures the preparation of draft and amending budgets and their publications; provides budgetary reporting on the general implementation of the budget and its transfers. Finally, Finance and Accounting provides financial advice and support to all Units in the Centre regarding budgetary commitments and budget monitoring.
Human Resources: Human Resources management promotes a supportive work environment that attracts, develops and motivates a multicultural and highly professional work force by providing high- quality services based on competent advice and communication with the ECDC’s staff and management. The activities include staff planning and reporting on an organisational basis, including implementation of ECDC's recruitment plans. It also includes the implementation of Implementing Rules and development of policies in line with the Staff Regulations. The Section is further responsible for the management of personnel and payroll administration, the management of staff health and well-being actions; performance management and reclassification processes as well as providing learning and development opportunities to ensure that organizational objectives are met and that staff receive accurate feedback and recognition on their performance.
Legal Services: The Section provides advice in legal matters related to the operational as well as administrative field of the Centre’s activities. The services further include the Data Protection Officer function, implementing the independence policies of the Centre and Access to Documents services.
Planning and Performance: The section ensures that the Centre is managed in a coherent, effective, and efficient way. It coordinates the development and implementation of the corporate strategy and oversees the full planning cycle, including the corporate reporting ( e.g. the Consolidated Annual Activity Report). It establishes, implements and enhances the Agency’s integrated management framework (IMF), thereby ensuring that processes, projects and services are compliant, fit for purpose and performed according to clearly defined requirements from the Agency’s management and stakeholders. As part of the continuous improvement of the organisational performance, it implements regular evaluations, coordinates audits, and evaluates and further improves the internal controls.
Procurement: The Section is the central reference entity for procurement and grant activities, providing operational support to all Units and assisting all internal clients in accomplishing their operational goals in a timely manner. The service includes maintaining compliance with the regulations, procedures and monitoring the Centre’s contracting for goods and services.





