Cholera worldwide overview
Monthly update as of 2 May 2025
Since 17 March 2025 and as of 02 May 2025, 16 111 new cholera cases, including 372 new deaths, have been reported worldwide.
Since 1 January 2025 and as of 2 May 2025, 111 359 cholera cases, including 1 562 deaths, have been reported worldwide. In comparison, since 1 January 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, 151 497 cholera cases, including 1 752 deaths, were reported worldwide.
New cases have been reported from Afghanistan, Angola, Bangladesh, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Ghana, Haiti, India, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Myanmar, Namibia, Nepal, Nigeria, Pakistan, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Yemen, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
The five countries reporting most new deaths are Angola (247), Sudan (62), Mozambique (29), Ethiopia (15) and Zimbabwe (10).
Geographical distribution of cholera cases reported worldwide from February 2025 to April 2025
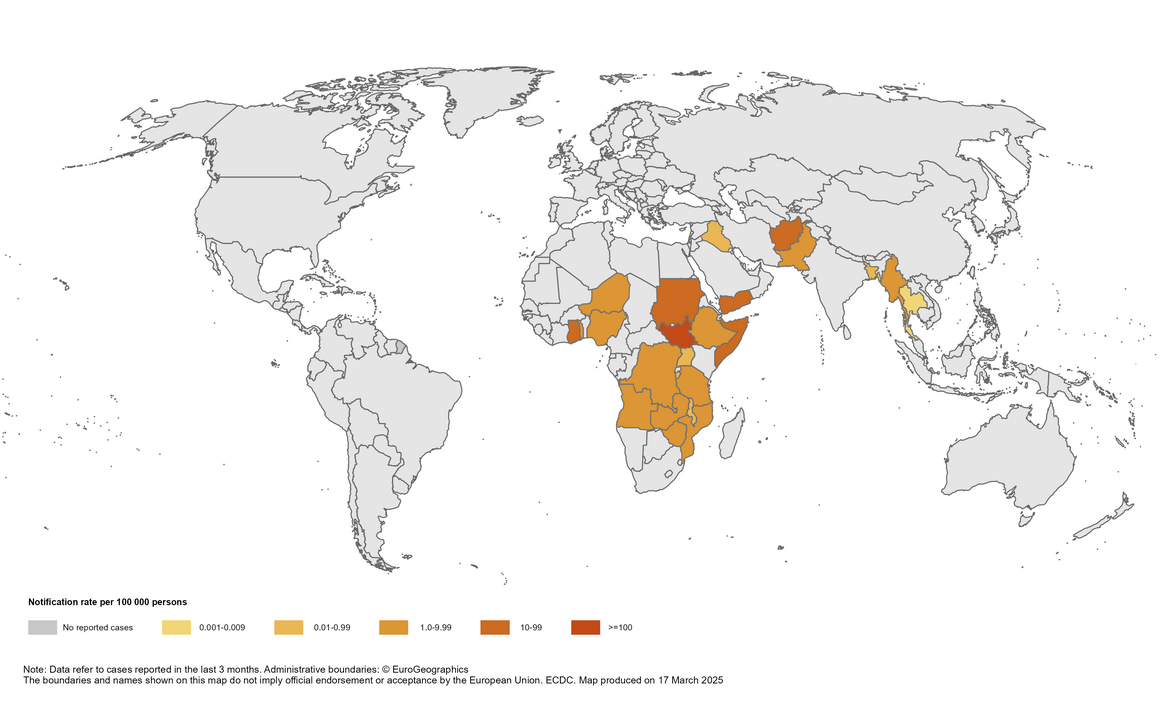
Asia
Afghanistan: Since 24 February 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 5 249 new cases, including two new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 19 652 cases, including 8 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 27 April 2024, 33 307 cases, including 16 deaths were reported.
Bangladesh: Since 31 December 2024 and as of 24 February 2025, 80 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 24 February 2025, 80 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 6 cases were reported.
India: Since 11 November 2024 and as of 03 March 2025, 93 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2025 and as of 03 March 2025, 93 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 15 April 2024, 1 320 cases, including four deaths were reported.
Myanmar: Since 20 January 2025 and as of 10 March 2025, 451 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 10 March 2025, 1 004 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Nepal: Since 23 September 2024 and as of 3 March 2025, 85 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 3 March 2025, 85 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Pakistan: Since 20 January 2025 and as of 10 February 2025, 1 809 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 10 February 2025, 4 038 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 24 March 2024, 5 313 cases were reported.
Yemen: Since 17 February 2025 and as of 24 February 2025, 296 new cases, including one new death has been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 24 February 2025, 10 080 cases, including 10 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 4 276 cases, including 23 deaths were reported.
Africa
Angola: Since 14 March 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 6 971 new cases, including 247 new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 14 090 cases, including 505 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Burundi: Since 24 February 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 34 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 129 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 163 cases were reported.
Democratic Republic of the Congo: Since 17 February 2025 and as of 10 March 2025, 3 862 new cases, including 69 new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 10 March 2025, 11 918 cases, including 240 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 13 555 cases, including 285 deaths were reported.
Ethiopia: Since 3 March 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 2 951 new cases, including 15 new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 3 808 cases, including 40 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 12 974 cases, including 97 deaths were reported.
Ghana: Since 12 March 2025 and as of 25 April 2025, 514 new cases, including 2 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2025 and as of 25 April 2025, 2 767 cases, including 14 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 02 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Kenya: Since 12 March 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 88 new cases, including five new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 125 cases, including six deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 29 March 2024, 186 cases, including one death was reported.
Malawi: Since 3 March 2025 and as of 20 March 2025, one new case has been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 20 March 2025, 91 cases, including three deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 243 cases, including three deaths were reported.
Mozambique: Since 3 February 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 2 787 new cases, including 29 new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 2 851 cases, including 29 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 7 371 cases, including 12 deaths were reported.
Namibia: Since 2 March 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 21 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 22 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Nigeria: Since 24 February 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 90 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 1 214 cases, including 28 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 559 cases, including seven deaths were reported.
Rwanda: As of 04 April 2025, four new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 04 April 2025, four cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Somalia: Since 20 January 2025 and as of 17 February 2025, 632 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 17 February 2025, 1 409 cases, including one death has been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 8 681 cases, including 87 deaths were reported.
South Sudan: Since 24 February 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 6 057 new cases, including 127 new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 25 179 cases, including 389 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Sudan: Since 03 March 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 1 965 new cases, including 62 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 8 568 cases, including 211 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 2 408 cases were reported.
Togo: Since 3 February 2025 and as of 24 February 2025, 23 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 24 February 2025, 161 cases, including four deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 2 May 2024, no cases were reported.
Uganda: Since 3 February 2025 and as of 03 March 2025, 52 new cases, including two new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 3 March 2025, 139 cases, including three deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 29 February 2024, 38 cases, including one death was reported.
United Republic of Tanzania: Since 17 February 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 323 new cases, including three new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 17 March 2025, 2 085 cases, including 16 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 2 503 cases, including 32 deaths were reported.
Zambia: Since 3 March 2025 and as of 15 April 2025, 148 new cases have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 15 April 2025, 463 cases, including nine deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 19 848 cases, including 611 deaths were reported.
Zimbabwe: Since 12 March 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 257 new cases, including 10 new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 30 April 2025, 505 cases, including 17 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 18 197 cases, including 371 deaths were reported.
America
Haiti: Since 5 January 2025 and as of 07 April 2025, 425 new cases, including two new deaths have been reported. Since 1 January 2025 and as of 07 April 2025, 794 cases, including 29 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2024 and as of 30 April 2024, 6 483 cases, including 119 deaths were reported.
ECDC assessment:
In 2025, cholera cases have continued to be reported in Africa and Asia, the Middle East and the Americas.
In this context, although the risk of cholera infection for travellers visiting these countries remains low, sporadic importation of cases to the EU/EEA is possible.
In the EU/EEA, cholera is rare and primarily associated with travel to endemic countries. Cholera reporting at the EU level is done on an annual basis, at the end of May for the year prior. In 2023, 12 confirmed cases were reported by five EU/EEA countries, while 29 were reported in 2022, two in 2021, and none in 2020. In 2019, 25 cases were reported in EU/EEA countries (including the United Kingdom). All cases had a travel history to cholera-affected areas.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), vaccination should be considered for travellers at higher risk, such as emergency and relief workers who may be directly exposed. Vaccination is generally not recommended for other travellers. Travellers to cholera-endemic areas should seek advice from travel health clinics to assess their personal risk and apply precautionary sanitary and hygiene measures to prevent infection. Such measures can include drinking bottled water or water treated with chlorine, carefully washing fruit and vegetables with bottled or chlorinated water before consumption, regularly washing hands with soap, eating thoroughly cooked food, and avoiding the consumption of raw seafood products.
Actions:
ECDC continues to monitor cholera outbreaks globally through its epidemic intelligence activities in order to identify significant changes in epidemiology and provide timely updates to public health authorities. Reports are published on a monthly basis. The worldwide overview of cholera outbreaks is available on ECDC's website.
All updates on Cholera
Disease page
Cholera
Cholera is an acute diarrhoeal infection caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholera of serogroups O1 or O139. Humans are the only relevant reservoir, even though Vibrios can survive for a long time in coastal waters contaminated by human excreta.




